The History of Silver and Its Future
Silver is sensible money and plays a critical role in the industry.
Share article:
In 1788, Founding Father Thomas Jefferson declared, "Paper is poverty… it is only the ghost of money, not money itself." The accomplished politician and author of America's Declaration of Independence was a staunch supporter of honest money.
 Honest money in Jefferson's days was 'real money free of debt, credit, and state issue money. Real money was at the time fully convertible to silver or gold. Jefferson and like-minded economists of the time equated honest money with independence and liberty.
Honest money in Jefferson's days was 'real money free of debt, credit, and state issue money. Real money was at the time fully convertible to silver or gold. Jefferson and like-minded economists of the time equated honest money with independence and liberty.
In 1787, George Washington wrote, "The wisdom of man, in my humble opinion, cannot at this time devise a plan by which the credit of paper money would be long supported; consequently depreciation keeps pace with the quantity of the emission, and articles, for which it is exchanged, rise in a greater ratio than the sinking value of the money. Wherein, then, is the farmer, the planter, the artisan benefited? The debtor may be because, as I have observed, he gives the shadow in lieu of the substance; and, in proportion to his gain, the creditor or the body-politic suffers".
 Unfortunately, The Founding Fathers' warning went unheeded, and since August 15, 1971, the world has been operating on a 100% fiat currency system. That was the day US President Richard Nixon cut all links between the US dollar and the gold standard.
Unfortunately, The Founding Fathers' warning went unheeded, and since August 15, 1971, the world has been operating on a 100% fiat currency system. That was the day US President Richard Nixon cut all links between the US dollar and the gold standard.
 All digital and physical central bank-issued currencies today are created on government computers and their printing presses, basing their values on citizens' confidence and faith.
All digital and physical central bank-issued currencies today are created on government computers and their printing presses, basing their values on citizens' confidence and faith.
Unfortunately, the history of all fiat monetary systems reveals that they all eventually fail. A fiat financial system's crash may be abrupt or undergo slow decay. A study done amongst a group of 775 fiat currencies shows that the life expectancy of a fiat currency system is 27 years. These fiat currencies were demonetized due to war, hyperinflation, or monetary reforms.
At least 20% of these currencies failed due to hyperinflation, while 21% lost their value due to the high costs of conflict and war. In addition, 24% of these currencies have suffered extensive monetary reforms, while the flames of independence wrecked 12%.
As per the rather hotly contested research, only 23% of the 775 fiat currencies that were part of the study are in circulation. Critics of the study, such as John Paul Koning, state that while this data is true, and these fiat currencies are demonetized, "they were replaced for political, economic, and cultural reasons... Existing currency holders weren't robbed. They were fairly compensated for this switch".
Silver Is Honest Money
That said, Koning, a monetary economics study, agrees that currencies have a variety of challenges. As an illustration, the oldest fiat currency in existence, the British Pound Sterling, has now lost over 99.5% of its value.
The silver-based Pound Sterling came into circulation in 1694 and was the most successful fiat currency for three centuries, acting as the world's reserve currency.
The Pound rose from continental Europe after the fall of the Roman empire. Anglo-Saxon England had embraced the Pound as its unit of currency by 775AD. In the 8th century, a pound was worth 1 pound weight of silver.
England's first monarch, Athelstan, introduced the sterling as the national currency in 928AD. He set up various currency mints around England to enhance the currency's circulation. The sterling's 1-pound weight of silver could purchase 15 head of cattle and was, therefore, extremely valuable.
The sovereign came to the fore in the Henry VII era in 1498. Before his reign, however, his predecessors had prioritized maintaining its coinage quality. In 1124, Henry I castrated at least half of all moneyers in England for minting counterfeit or substandard coins.
On the other hand, Henry II held the annual “Trial of the Pyx," a courtroom-esque ceremony to test the cons' quality. By 1282, the Pound's silver content had lowered from 1 pound weight of silver to 92.5%. The reduction of silver content would improve the durability of the malleable metal. The 92.5% content was referred to as sterling silver.
Henry VIII was the first monarch, however, to drastically lower the Pound's silver content. The act was referred to as the Great Debasement. Fortunately, in 1560, Elizabeth I reestablished the Pound's value, giving it ample stability into the 19th century.
In 1690, King William III's navy lost to France. In need of quick war funding, King William III established the Bank of England in 1694. The bank brought £1.2m into circulation in 12 days. About 50% of this fiat currency was utilized in rebuilding navy infrastructure.
In an attempt to manage the value of the pound sterling, the UK defined the value of the sterling in gold rather than silver. That said, the 1797 Bank Restriction Act dropped the convertibility of banknotes to gold, limiting access to quick and cheap loans that would finance the British government's war expenses.
The Bank Restriction Act would save the central bank from bankruptcy since the number of pounds in circulation had surpassed the gold backing it. That said, the damage done by the constant creation of fiat money had debased the pound sterling significantly by the end of the Napoleonic wars in 1814.
Consequently, the gold standard was re-established, reinstating a fixed exchange between the BoE banknotes and gold. Then the Pound began its steep depreciation, and the taxpayers assumed massive public debt.
However, the gold standard had a positive outcome for creditors, guaranteeing them repayment in a currency with stable purchasing power anchored to gold. Moreover, English public finance credibility strengthened as deflation automatically enlarged the real cost of public debt.
Interestingly, the British majority was against the return to the gold standard, advocating for the Pound's age-old and silver-based benefits. That said, 90% of all British parliamentarians at the time had public debt.
The average debt threshold was £10,355 and had a £310 interest rate. A senior civil servant's annual wage was £219 in 1819. The aristocrats benefited the most from the gold standard as it guaranteed the value of their monetary assets.
The Cost of Currency Debasement
The war era did a number on the Pound as the UK first dropped the gold standard to print more fiat for its war efforts. Unfortunately, the heavy issuance of fiat led to high inflation in the World War 1 period leading to a significant devaluation of the Pound.
In 1914, one Pound was worth $4.70. Then, Winston Churchill embraced the gold standard giving the Pound a $4.86 value. But Britain dropped the gold standard in 1931, and the Pound's value had fallen to $3.69.
At the start of WWII in 1940, led by British forces, the British government adopted the USD as the peg value of the Pound. However, the 1967 British economic crisis led to more currency debasement; by 1976, one Pound was worth $1.7. The Pound was worth $1.33 in 2016, as the UK left the EU.
Consequently, between the 15th century and the 2000s, the Pound's purchasing power had lost its value four-hundred-fold. Inflation, on the other hand, had risen 118 times between 1750 and 1998.
Silver Is the Future of Real Value Investments
Interestingly, Rome also fell when its emperors began to debase the value of their silver-based currency. The Roman denarius minted in 211 BC had 4.5 grams of silver. Faced with massive war and conquest budgets, various Roman emperors began to debase the denarii.
In Nero's era, from AD37 to AD68, one denarius had 3 grams of silver. Then, between AD193 to AD235, several emperors debased the denarius's value by 50%, giving it a 2.60 grams weight. Finally, in 274 AD, Emperor Aurelian introduced the double denarii, which was only 5% silver.
Since coins had less and less silver, citizens and their rulers alike lost confidence in them. Soon larger parts of Rome abandoned silver coins storing their wealth in gold. But unfortunately, gold is a poor medium of exchange, and the rising crisis of confidence in the denarii led to the degeneration of major trade cities and routes.
Coin debasement and the eventual disintegration of trade routes ended the Roman Empire by 476 AD. In its place rose smaller empires such as the Britons, Scots, and Anglo Saxons. However, Mercian king Offa first minted a 22.5 grains silver penny in 756AD, introducing silver-backed currencies to the English. This coin was the predecessor of the Saxon pound that gave way to the Pound.
Age-old silver-based monetary systems held their real value until they encountered debasement by government officials. In 1992, Milton Friedman said abandonment of the bitamellic standard in 1878 led to more price instability than anticipated and was a mistake that had highly adverse consequences.
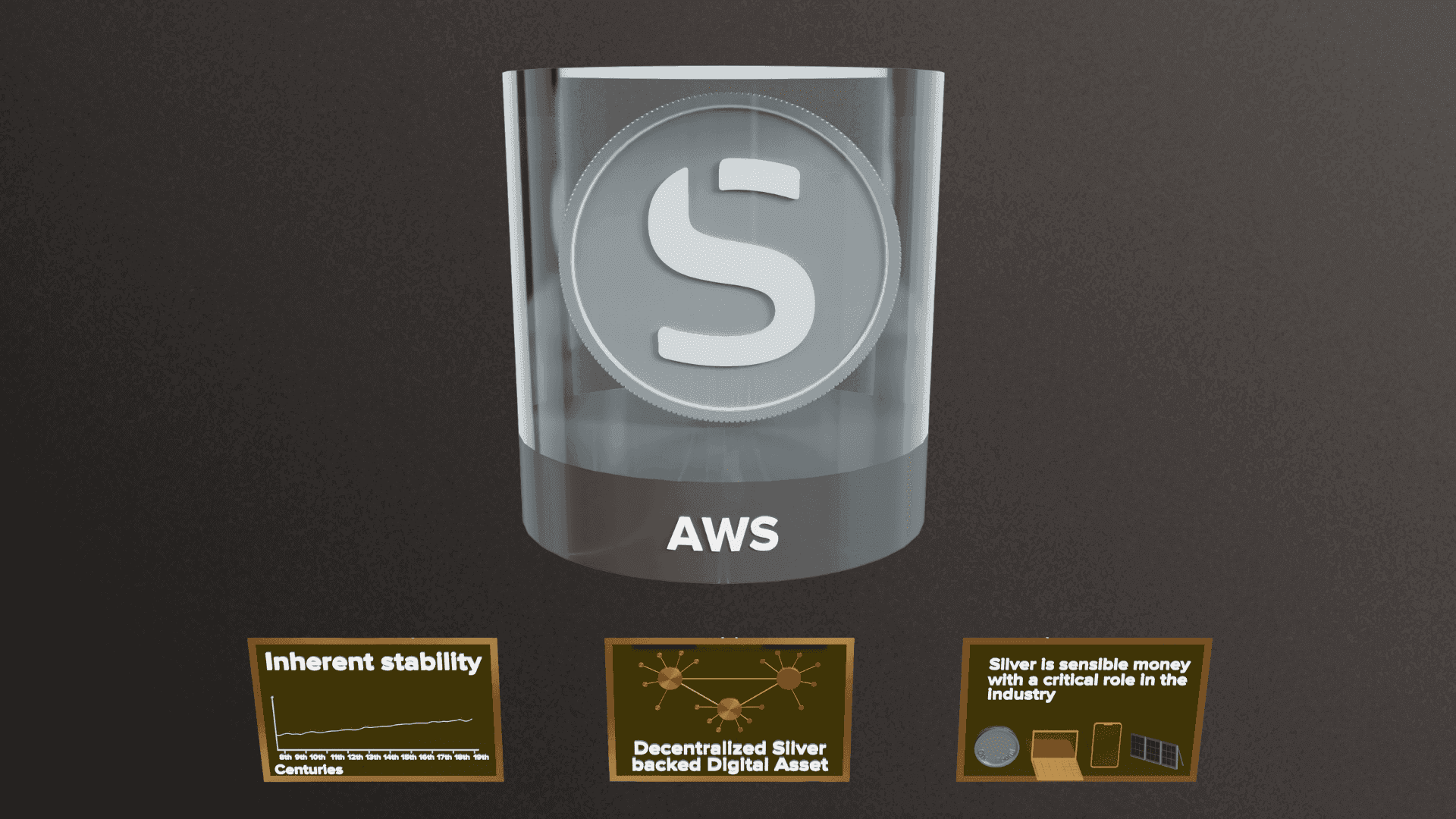
Introducing Silver-Backed Crypto: AurusSILVER (AWS)
Silver is sensible money and plays a critical role in the industry. It has much more than monetary value. Its use is underpinning the growing computing and solar panel industries. There is, therefore, no better time to hold silver in your portfolio.
Fortunately, an effortless, blockchain secure, quick, and decentralized silver investment process exists. The Aurus Protocol's AurusSILVER (AWS) tokens are 100% backed by silver. In addition, the AurusSILVER token runs on the Ethereum blockchain and opens access to a wide range of DeFi yield farming opportunities.
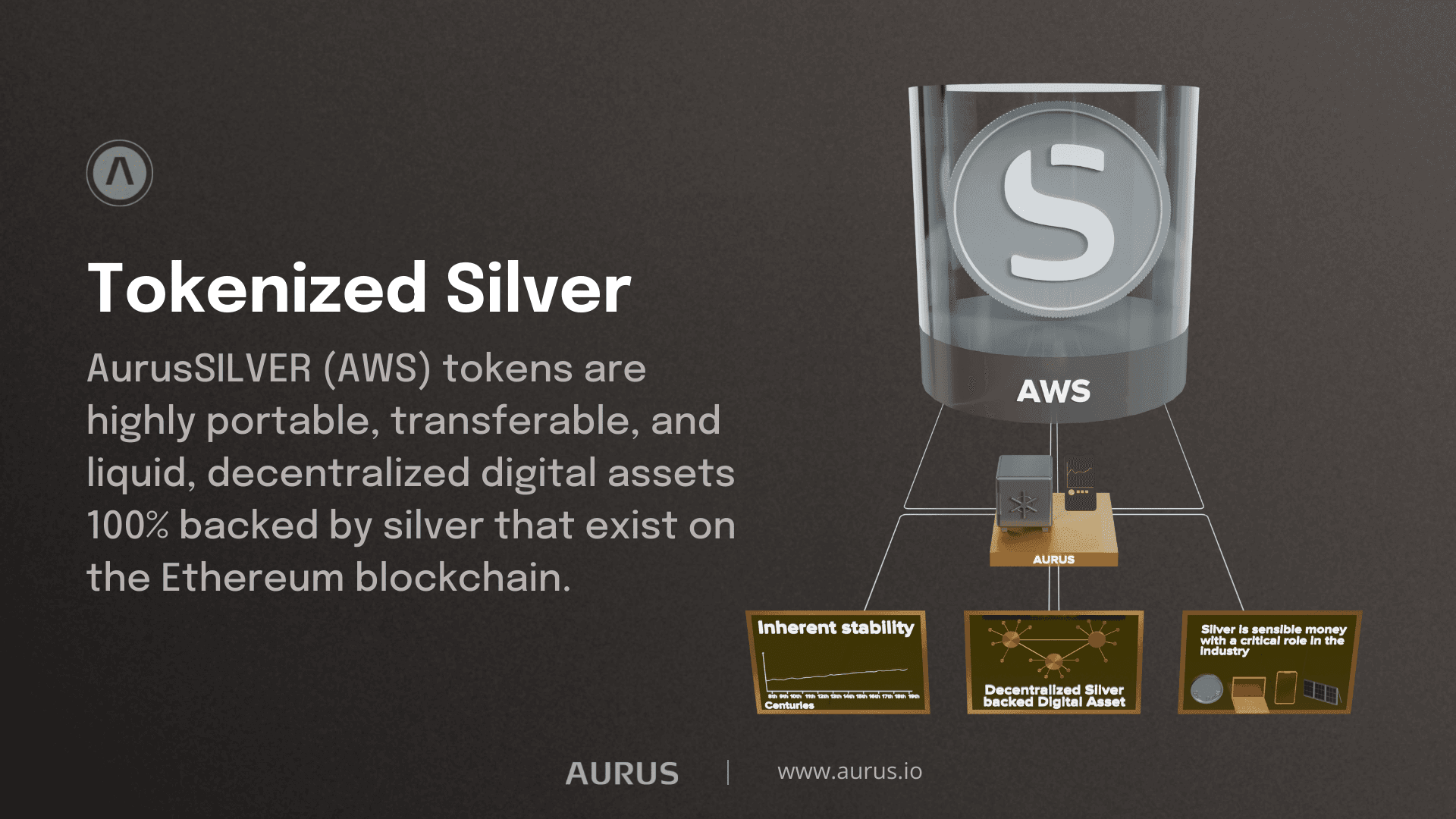 As the most liquid from of silver, AurusSILVER can be used as as the easiest way to accumulate and preserve wealth, as a hedge against volatile markets, and ultimately as a reliable alternative to unstable fiat currencies. Since the story of silver as money is yet to be written as fiat currencies undergo constant debasement. Silver has thousands of years of history backing its performance, and its diverse industry applications will uphold its value in the future.
As the most liquid from of silver, AurusSILVER can be used as as the easiest way to accumulate and preserve wealth, as a hedge against volatile markets, and ultimately as a reliable alternative to unstable fiat currencies. Since the story of silver as money is yet to be written as fiat currencies undergo constant debasement. Silver has thousands of years of history backing its performance, and its diverse industry applications will uphold its value in the future.
Buy and redeem AurusSILVER via Aurus partnered bullion dealers
Follow Aurus: Website | Twitter | Telegram | LinkedIn | Youtube | Newsletter